/**
* 46. Permutations
* Given an array nums of distinct integers, return all the possible permutations.
* You can return the answer in any order.
* Example 1:
* Input: nums = [1,2,3]
* Output: [[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
*/
See my solution on github here: https://github.com/zcoderz/leetcode/blob/main/src/main/java/backtracking/Permutations.java
This is a common question and its important to understand logic for permutations. The algorithm is rather trivial and explained below:
- Write a recursive method where you swap the current index iteratively with another index where the other index starts from current index and moves to the end of the collection.
- After each swap you recurse into the same method to swap from the index one right of the given index
- At end of recursion, you back track via reversing the swap done in 1
- Once the index reaches end of the collection, you record the current collection as one form of permutation.
You can look up more info about permutations here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Permutation#k-permutations_of_n
The below image from leetcode helps explain the recursion tree visually.
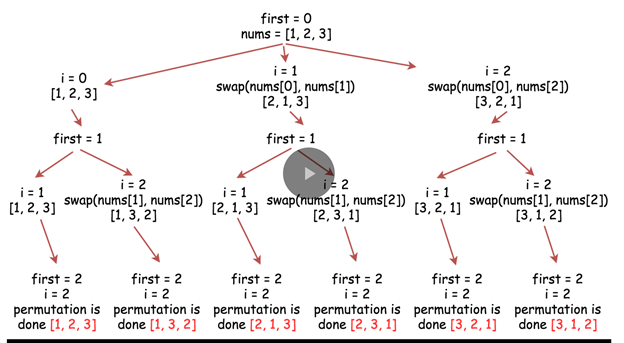
Here is the code:
void execute(int length, int index, List<Integer> nums, List<List<Integer>> retList) {
if (index == length) {
retList.add(new ArrayList<>(nums));
}
for (int i = index; i < length; i++) {
Collections.swap(nums, index, i);
execute(length, index + 1, nums, retList);
Collections.swap(nums, index, i);
}
}